On Insults in Dialogue
Here I am, late to the party, but this article on Skepchick got me thinking. Apparently, last month, there was a big blow-up about ableist language used in another post, and this Skepchick article addresses the issue. I don’t agree with much of the article, and I don’t hang out in the Skeptic community, but all that is really beside the point. What I find so interesting is the amount of words spent — both in the article and in the comments section — on the whole problem of whether it’s okay to use an ableist insult, whether anyone should care whether people are triggered, and whether we should all just get over being offended.
To me, words like “idiot” and “moron” and “stupid” are ableist, so I think that people were absolutely right to raise the issue. However, I think that there is something quite — I don’t know, odd? — about arguing over what kind of insults are allowed in dialogue. The whole problem could be solved by sticking to content, respecting the dignity of other people, and staying away from insults altogether, yes? Then you’d never end up with an ableist insult coming out of your mouth or off the keys of your computer.
The purpose of an insult is to hurt, to shame, and to demean. So is it any surprise that people who are uninvolved in the argument end up as collateral damage? Is it any wonder that sexism, racism, homophobia, transphobia, and ableism start creeping in when the insults start flying? After all, if an insult is meant to hurt, to shame, and to demean, then what better way to do it than to make implicit comparisons to people who are already hurt, shamed, and demeaned?
This is why I do my best to stay away from insults and why I’m not interested in anyone coming on my blog and launching them. It’s not just painful to the people involved; it has the potential to add to the marginalization of already marginalized people. And no, I don’t think we ought to be compiling lists of non-bigoted insults. I think we ought to be able to talk to one another with dignity about how to fix the problems in the world we live in.
But obviously, I’m a dreamer. Being harsh and cruel is so acceptable now that I often wonder why I even write these kinds of words. And then I remember that I write them so that others who feel as I do will know that they’re not alone. I write for people like myself, who would rather have an insult be a rare event and not a common and acceptable mode of communication.
I hope our culture can move back to valuing respectful dialogue. Of course, there is no reason to romanticize the past. It’s true that there have always been all kinds of disrespect and indignities visited upon millions of people, and respectful dialogue was not the experience of the many. I’ve experienced disrespect, indignity, and assault in my own life, and I come from a people that experienced it for many centuries. What I remember, though, from my earlier years as an activist, is that people who wanted to create a just world valued respecting people. They valued raising up people who were not respected into the light of dignity. They felt that the only way to create peace and justice was to model it. What I see now is exactly the opposite — that we’ve given into the idea that, because the world is a brutal and violent place, it’s somehow all right to be nasty with each other.
I don’t see our society valuing respectful dialogue any time soon — perhaps not even in my lifetime. I’m realizing that what I’ve worked so hard to do all of my adult life — to engage in civil dialogue while staying rooted in all of my emotions — is no longer of value to most people in the society I live in. This realization saddens me more than words can say.
© 2014 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Passing and Disability: Why Coming Out as Disabled Can Be So Difficult
Yesterday was National Coming Out Day. I officially came out as bisexual, and it was a celebration. No angst. No fear. No second thoughts. Just a celebration.
It was a such a contrast with coming out as disabled at the end of 2008, with all of the fear and dread that attended that decision. There have been many times since then that I’ve thought that coming out as disabled was the worst decision I’d ever made in my life. If I could have put the toothpaste back in the tube at those moments, I would have.
Of course, I’m a few years down the road now and feel much more comfortable, proud, and confident. But oh, what a process! And of course, the process never ends. I always have internalized shame, and hatred, and fear to root out of my head. And I still have to deal with a world of people who don’t understand the physical and social experience of disability. But in general, I navigate these waters much better than I did at the outset.
It’s very difficult to come out as disabled, I think, because we face the dual reality that most people a) hate our bodies absolutely unapologetically and b) consider that hatred entirely natural. It’s for this reason that they can use disability slurs constantly and think nothing of it. It’s for this reason that they can segregate and exclude us as though we’re substandard merchandise to return to the manufacturer. It is still considered natural to react with revulsion against us in a way that other groups have fought against more successfully — not entirely successfully, obviously, but more successfully.
Partly, we face this hatred because our culture worships control and denies the fragile and ever-changing life of the body. Partly, we face this hatred because the medical model has taken over as a metaphor for human life. People are no longer evil. People no longer make bad choices. People are no longer victimized by oppression. People no longer act out of ignorance, or selfishness, or greed. No. Now they’re sick, crazy, brain-dead, retarded, mentally ill, have low IQs, and on and on.
In the face of this hatred, it’s very, very difficult to convince people that you love your disabled body because it’s the one you live in. You say that you love your body, and people look at you as though you don’t quite understand your own reality.
My body hurts a lot these days. But I still love it. It’s the body I was born with. It enables me to experience life. Without it, I’d have no life at all. I might not love every sensation in my body, but I love my body, even on the hardest days, because it gives me life.
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Disability as the Ultimate Insult
I heard a disability slur the other day that I’d never run across before. It was in a social justice context (surprise surprise), and one commenter said to another: “If you really believe that, you probably shouldn’t go out without a carer.”
Ah, yes. It’s the ultimate insult: Being disabled and needing a caregiver. Wow. Is that the hierarchy in which most people live? Yes. Could the hatred be any clearer? I don’t think so. That kind of thinking speaks volumes about how even the most enlightened radical folk see disabled people — which makes such radical folk not radical at all, but really quite mainstream.
I am always pushing back against this kind of talk. I am always asking for people to stop using disability slurs. But on days like today, I wonder whether I shouldn’t just be quiet and let people have at it. At least, that way, the degree to which they despise us would be out in the open.
Perhaps I should just collect all of these instances and publish them. That way, no one can say, “Oh, no, no, no, no. Don’t be ridiculous. There is no such thing as disability hatred.”
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Doing Social Justice: Thoughts on Ableist Language and Why It Matters
The economy has been crippled by dept.
You’d have to be insane to want to invade Syria.
They’re just blind to the suffering of other people.
Only a moron would believe that.
Disability metaphors abound in our culture, and they exist almost entirely as pejoratives. You see something wrong? Compare it to a disabled body or mind: Paralyzed. Lame. Crippled. Schizophrenic. Diseased. Sick. Want to launch an insult? The words are seemingly endless: Deaf. Dumb. Blind. Idiot. Moron. Imbecile. Crazy. Insane. Retard. Lunatic. Psycho. Spaz.
I see these terms everywhere: in comment threads on major news stories, on social justice sites, in everyday speech. These words seem so “natural” to people that they go uncritiqued a great deal of the time. I tend to remark on this kind of speech wherever I see it. In some very rare places, my critique is welcome. In most places, it is not.
When a critique of language that makes reference to disability is not welcome, it is nearly inevitable that, as a disabled person, I am not welcome either. I might be welcome as an activist, but not as a disabled activist. I might be welcome as an ally, but not as a disabled ally. I might be welcome as a parent, but not as a disabled parent. That’s a lot like being welcomed as an activist, and as an ally, and as a parent, but not as a woman or as a Jew.
Many people have questions about why ableist speech matters, so I’ll be addressing those questions here. Please feel free to raise others.
1. Why are you harping so much on words, anyway? Don’t we have more important things to worry about?
I am always very curious about those who believe that words are “only” words — as though they do not have tremendous power. Those of us who use words understand the world through them. We use words to construct frameworks with which we understand experience. Every time we speak or write, we are telling a story; every time we listen or read, we are hearing one. No one lives without entering into these stories about their fellow human beings. As Arthur Frank writes:
“Stories work with people, for people, and always stories work on people, affecting what people are able to see as real as possible, and as worth doing or best avoided. What is it about stories – what are their particularities – that enables them to work as they do? More than mere curiosity is at stake in this question, because human life depends on the stories we tell: the sense of self that those stories impart, the relationships constructed around shared stories, and the sense of purpose that stories both propose and foreclose.” (Frank 2010, 3)
The stories that disability metaphors tell are deeply problematic, deeply destructive, and deeply resonant of the kinds of violence and oppression that disabled people have faced over the course of many centuries. They perpetuate negative and disempowering views of disabled people, and these views wind their ways into all of the things that most people feel are more important. If a culture’s language is full of pejorative metaphors about a group of people, that culture is not going to see those people as fully entitled to the same housing, employment, medical care, education, access, and inclusion as people in a more favored group.
2. What if a word no longer has the same meaning it once did? What’s wrong with using it in that case?
Ah yes. The etymology argument. When people argue word meanings, it generally happens in a particular (and largely unstated) context. With regard to ableist metaphors, people argue that certain meanings are “obsolete,” but such assertions fail to note the ways in which these “obsolete” words resonate for people in marginalized groups.
For example, I see this argument a great deal around the word moron, which used to be a clinical term for people with an intellectual disability. I have a great-aunt who had this label and was warehoused in state hospitals for her brief 25 years of life. So when I see this word, it resonates through history. I remember all of the people with this designation who lived and died in state schools and state mental hospitals under conditions of extreme abuse, extreme degradation, extreme poverty, extreme neglect, and extreme suffering from disease and malnutrition. My great-aunt lay dying of tuberculosis for 10 months under those conditions in a state mental hospital. The term moron was used to oppress human beings like her, many of whom are still in the living memory of those of us who have come after.
Moron — and related terms, like imbecile and idiot – may no longer be used clinically, but their clinical use is not the issue. They were terms of oppression, and every time someone uses one without respect for the history of disabled people, they disrespect the memory of the people who had to carry those terms to their graves.
3. What’s wrong with using bodies as metaphors, anyway?
Think about it this way: Consider that you’re a woman walking down the street, and someone makes an unwanted commentary on your body. Suppose that the person looks at you in your favorite dress, with your hair all done up, and tells you that you are “as fat as a pig.” Is your body public property to be commented upon at will? Are others allowed to make use of it — in their language, in your hearing, without your permission? Or is that a form of objectification and disrespect?
In the same way that a stranger should not appropriate your body for his commentary, you should not appropriate my disabled body — which is, after all, mine and not yours — for your political writing or social commentary. A disabled body should not appear in articles about how lame that sexist movie is or how insane racism is. A disabled body should be no more available for commentary than a nondisabled one.
The core problem with using a body as a metaphor is that people actually live in bodies. We are not just paralyzed legs, or deaf ears, or blind eyes. When we become reduced to our disabilities, others very quickly forget that there are people involved here. We are no longer seen as whole, living, breathing human beings. Our bodies have simply been put into the service of your cause without our permission.
4. Aren’t some bodies better than others? What’s wrong with language that expresses that?
I always find it extraordinary that people who have been oppressed on the basis their physical differences — how their bodies look and work — can still hold to the idea that some bodies are better than others. Perhaps there is something in the human mind that absolutely must project wrongness onto some kind of Other so that everyone else can feel whole and free. In the culture I live in, disabled bodies often fit the bill.
A great deal of this projection betrays a tremendous ignorance about disability. I have seen people defend using mental disabilities as a metaphor by positing that all mentally disabled people are divorced from reality when, in fact, very few mental disabilities involve delusions. I have seen people use schizophrenic to describe a state of being divided into separate people, when schizophrenia has nothing to do with multiplicity at all. I have seen people refer to blindness as a total inability to see, when many blind people have some sight. I have seen people refer to deafness as being locked into an isolation chamber when, in fact, deaf people speak with their hands and listen with their eyes (if they are sighted) or with their hands (if they are not).
Underlying this ignorance, of course, is an outsider’s view of disability as a Bad Thing. Our culture is rife with this idea, and most people take it absolutely for granted. Even people who refuse to essentialize anything else about human life will essentialize disability in this way. Such people play right into the social narrative that disability is pitiful, scary, and tragic. But those of us who inhabit disabled bodies have learned something essential: disability is what bodies do. They all change. They are all vulnerable. They all become disabled at some point. That is neither a Good Thing nor a Bad Thing. It is just an essential fact of human life.
I neither love nor hate my disabilities. They are what they are. They are neither tragic nor wonderful, metaphor nor object lesson.
5. Disabled people aren’t really oppressed. Are they?
Yes, disabled people are members of an oppressed group, and disability rights are a civil rights issue. Disabled people are assaulted at higher rates, live in poverty at higher rates, and are unemployed at higher rates than nondisabled people. We face widespread exclusion, discrimination, and human rights violations. For an example of what some of the issues are, please see the handy Bingo card I’ve created, and then take some time over at the Disability Social History Project.
6. If my disabled friend says it’s okay to use these words, doesn’t that make it all right to use them?
Please don’t make any one of us the authority on language. It should go without saying, but think for yourself about the impact of the language you’re using. If you stop using a word because someone told you to, you’re doing it wrong. It’s much better if you understand why.
7. I don’t know why we all have to be so careful about giving offense. Shouldn’t people just grow thicker skins?
For me, it is not a question of personal offense, but of political and social impact. If you routinely use disability slurs, you are adding to a narrative that says that disabled people are wrong, broken, dangerous, pitiful, and tragic. That does not serve us.
8. Aren’t you just a member of the PC police trying to take away my First Amendment rights?
No. The First Amendment protects you from government interference in free speech. It does not protect you from criticism about the words you use.
9. Aren’t you playing Oppression Olympics here?
No. I’ve never said that one form of oppression is worse than another, and I never will. In fact, I am asking that people who are marginalized on the basis of the appearance or functioning of their bodies — on the basis of gender identity, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, class, size, and disability — get together and talk about the ways in which these oppressions weave through one another and support one another.
If you do not want disability used against your group, start thinking about what you’re doing to reinforce ableism in your own speech. If you do not want people of color to be called feeble-minded, or women to be called weak, or LGBT people to be called freaks, or fat people to be called diseased, or working-class people to be called stupid — all of which are disability slurs — then the solution isn’t to try to distance yourself from us and say, No! We are not disabled like you! The solution is to make common cause with us and say, There is nothing wrong with being disabled, and we are proud to stand with you.
10. Why can’t we use disability slurs when the target is actually a nondisabled person?
To my knowledge, the president of the United States is not mentally disabled, and yet his policies have been called crazy and insane. Most Hollywood films are made by people without mobility issues, and yet people call their films lame. Someone who has no consciousness of racism or homophobia will be called blind or deaf to the issues, and yet, such lack of consciousness runs rampant among nondisabled people.
So why associate something with a disability when it’s what nondisabled people do every single day of the week? As far as I can see, lousy foreign policy, lousy Hollywood films, and lousy comments about race and sexual orientation are by far the province of so-called Normal People.
So come on, Normal People. Start owning up to what’s yours. And please remember that we disabled folks are people, not metaphors in the service of your cause.
References
Disability Social History Project. http://www.disabilityhistory.org. Accessed September 14, 2013.
Facebook. “Disability and Representation.” https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=638151876196123&set=a.535870946424217.126038.447484845262828&type=1. Accessed September 14, 2013.
Frank, Arthur W. Letting Stories Breathe: A Socio-Narratology. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press, 2010.
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Holding Fast To My Own Experience
I’ve been wanting to write this post for a long time, but it’s taken me awhile to get enough distance on the whole issue to be able to write about it out of power rather than out of fear.
As many of you know, I’ve done a lot of work critiquing research into autism and empathy — both in my academic life and online at my Autism and Empathy site. One of the driving factors behind this work was an experience I’ve been afraid to talk about. To put it as briefly as possible: the research conclusions surrounding an alleged lack of empathy in autistic people made me question when I am really empathetic at all, and they filled me with doubt and dread for a very long time.
I’ve spent much of my adult life describing myself as an empath, and I have always read emotional and social process very well. But then my autism diagnosis came along and voila! I was supposed to be deficient in empathy. In fact, I read study, after study, after study showing that autistic people have an empathy disorder, and the cold voices of authority started getting into my head. That was bad. Very bad. What Sartre wrote about the Jewish people applied equally well to me as an individual:
“They have allowed themselves to be poisoned by the stereotype that others have of them, and they live in fear that their acts will correspond to this stereotype.” (Sartre 1960, 95)
“Poisoned” is right. I was sick with fear and doubt. A year or two ago, I finally got up the courage to check the whole empathy question out with the people who know me best: my husband and my kid. I started with the kid, who was still a teenager at the time. I said, “Ash, do you think I’m empathetic?”
Ash looked at me in a way that only teenagers can look at mothers: with a mixture of impatience, love, and something bordering on anger for wasting their time. With an eye roll, my kid spoke the following immortal words;
“Mom. YES. You are very empathetic. Exhibit A: MY ENTIRE LIFE.”
I felt relieved. Later in the evening, after my husband came home, I related my conversation with Ash and poured out my relief as he made himself toast at the kitchen counter. His response? He was uncharacteristically brief. “Good,” he said. “No need to ask this question again.”
Somehow, those two conversations allayed my doubts. I couldn’t write about it for a long time, though. I couldn’t acknowledge publicly the kinds of doubt the research had raised in me. But I can do so now, because I’ve come to understand that I wasn’t just having an experience of personal insecurity. I’ve come to realize that this kind of doubt is common for people in all kinds of marginalized groups. I’ve finally seen the ways in which those with cultural authority speak for us, ask us to prove our experience with numbers and graphs and research papers, and then tell us that our experience means nothing because it doesn’t match their findings.
The rather obvious conclusion to draw from research findings that don’t match reality is that the research findings are wrong, but of course, that rarely happens. The research findings take on the authority of truth, and the experiences of people who actually live in the bodies being researched mean very little.
Put another way: The truth means very little. The story that is constructed, however, means everything, and we find ourselves spending massive amounts of energy arguing against the story, both within ourselves and with everyone else. Patricia Williams writes about studies on race in a way that rings true for me as I recall all the many hours I’ve spent refuting autism research:
“One of the great difficulties of pseudo-science is that it is so hard to refute just by saying it isn’t so. The logical structure — if not the substance — of pseudo-science posits what purports to be fact; it requires counter-fact to make counter-arguments. Black people find themselves responding endlessly to such studies before we can be heard on any other subject; we must credentialize ourselves as number-crunching social scientists quickly in order to be seen as even minimally intelligent… Real numbers, real science — it’s what school teaches us to revere. And it makes anyone who knows the great messy, unprovable contrary, who knows the indecipherable complexity of black or white people, who knows the reality and the potential of all humanity — us silly egalitarians — it makes us unintelligent, uninformed, powerless, and naïve.” (Williams 1998, 49-50)
“Real numbers, real science” — how do these things even begin to compete with the delicious, messy, complex, living, breathing nature of human experience? They don’t. They can’t. They can never even come close. They only put us into hierarchies: black/white, normal/abnormal, able/disabled, and so many others.
Do I regret that I spent so many hours critiquing the research? Do I wish I’d said instead, “To hell with your studies, to hell with your questionnaires, to hell with the careers you’ve built on the backs of people like me”? In some ways, yes. But in other ways, I am glad to have been able to spend some time in the belly of the monster, because I got to know its way of being very, very well and I got to see how very barren the belly is.
The monster doesn’t scare me anymore. It’s been banished. And when people try to raise the monster back up, I find myself wondering why they’re wasting their time believing in an apparition.
References
Sartre, Jean-Paul. Anti-Semite and Jew. New York, NY: Grove Press, 1960.
Williams, Patricia. Seeing a Color-Blind Future: The Paradox of Race. New York, NY: Farrar, Strauss, and Giroux, 1998.
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
I Am Now Officially a Bitter Crip!
As many of you know, I have been working very hard at being a bitter crip. I critique the hell out of everything. I write about inspiration porn. I analyze media stories about disability. I complain loudly at the merest hint of ableist rhetoric. I even write about people giving me grief at the post office and in the check-out line.
And yet, until yesterday, I’d never been called a bitter crip. Not once. Not ever. After working so hard at it for so long, I’d just never received the recognition I craved. It was all a trial and a tribulation.
I was beginning to lose hope. After all, I’m 55 years old and I’ve been in a state of entirely justifiable outrage deep and abiding bitterness for a long time. I thought, holy crap, if I haven’t made it to bitter crip status at this point, maybe I should just give it up and post cat videos.
But then I wrote a piece about a beer commercial and… Wow! You should see the comments I got! Some of them actually made it out of moderation and onto my blog. Others were in such thorough violation of my simple and intuitive “Don’t be nasty to the blogger” policy that I didn’t let them through. But still! I thought I’d reached the golden pinnacle of bitter cripdom when I received the following comment on Thursday:
“Jesus, you are a fucking miserable person. That was a nice ad with a nice message. I think you’ve expressed your own insecurities far more than you’ve expressed any flaws in the advertisement.”
Being called a “fucking miserable person” is pretty close to being called a bitter crip, but it’s not quite the same. In my desperation, I kept trying to make it the same, but who was I fooling? I felt like such a wannabe.
But then on Friday, I finally made it. I was so excited! Here is the comment that put me over the top:
“OMG!! Are you for real??? Bitter, at all??? This was an incredible commercial. No, ‘regular guys’ wouldn’t be so agile in using wheelchairs to play basketball, but the thought that they might attempt it so that their friend, who depends on a wheelchair can play a legitimate game of basketball with them is the message!!!!!!! You don’t get that???
You must live a very sad, sorry, pitiful life… wheelchair or no wheelchair…”
DINGDINGDINGDINGDING! Bonus points for gratuitous use of exclamation points and question marks!!!!!!
Gosh! It’s such a moment! And so unexpected! I hardly know what to say. I could never have gotten here on my own, that’s for sure. It takes a village to raise a bitter crip, and thanks are due all around.
Thank you to all of my fellow bitter crips for being such INSPIRING role models. OMG! There are too many of you to list here, but you know who you are!
Thank you to all of the people who have left nasty comments on my blogs over the years. You have kept hope alive that, one day, I might enter the ranks of bitter cripdom!
Thank you to all of the people who have told me, throughout the course of my life, that I should just be grateful and shut the fuck up and stop thinking about things so much. Without you, I’d never have dreamed this big!
And finally, to the lovely lady who called me a bitter crip: Thank you! This is a moment that I will cherish forever.
Let the celebration begin!
(You can find the lyrics here.)
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Ableism on the Left is Still Ableism
If you consider yourself politically progressive, chances are that you firmly believe that racism, classism, misogyny, homophobia, anti-Semitism, Islamophobia, and all other forms of bigotry have no place in political discourse or civil society. As a fellow progressive, I wholeheartedly agree.
So why, oh why, is ableism perfectly fine with you? Why, oh why, do you find it perfectly all right to engage in bigotry against disabled people for the purpose of your political agenda?
May I share a representative example? Consider the following graphic, which was posted to a Facebook page called The Republican Party- Is Corruption, Greed & Lies and The Real Evil Empire.
Source: Facebook [The graphic consists of a black-and-white photograph of former president Ronald Reagan sitting with one foot resting on a round table. The table has two stacks of paper on it; some of the pages are draped over the stacks. Behind him is the front of a house and two leafy trees. The text reads: "Closed Down Mental Institutions. Got Shot by Nutjob. Karma."]
Now, for what it’s worth, I’m willing to believe that you mean no harm. I’m willing to believe that, despite your progressive credentials, you are blissfully unaware of the bigotry you carry against disabled people. In fact, I am more than willing to believe that, despite your progressive credentials, you have no idea what ableism is.
Allow me enlighten you.
Ableism is the belief that nondisabled people are worthier human beings than disabled people. Ableism is the belief that nondisabled people should have a different set of rights than disabled people. Ableism is the belief that disabled people should be segregated, patronized, sneered at, laughed at, abused, and dismissed.
But it’s more than a belief. It plays itself out in systemic injustices — in high rates of unemployment, in high rates of poverty, and in high rates of abuse. It plays itself out in exclusion — social exclusion, economic exclusion, and architectural exclusion. It plays itself out daily in the ways in which disabled people become metaphors for social ills and our culture’s deepest fears.
In others words, it plays itself out just as any other form of bigotry plays itself out — as a series of assumptions, as a set of structural inequities, and as a barrage of microaggressions that take place every hour of every day. And as is true for any other form of bigotry, engaging in ableism while meaning no harm is not a defense against actually doing it.
The graphic you posted is ableist. Why?
Because calling a mentally ill person a nutjob is ableist.
Because implying that mentally people are all violent offenders is ableist.
Because suggesting that mentally ill people who have committed no crime should be incarcerated is ableist.
Because allowing comments in response to this graphic like “Ooh! Ooh! I’ve got one! What’s Reagan’s favorite vegetable? James Brady!” without calling them out is ableist.
Wake up, my fellow progressives. You can’t root out bigotry in this world while engaging in it. You ought to know that.
© 2013 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Scapegoating Schizophrenia: Paul Steinberg’s Shameful New York Times Op-Ed Column
The scapegoating continues.
This week’s New York Times Op-Ed page features an utterly irresponsible article in which psychiatrist Paul Steinberg baselessly blames schizophrenia for mass shootings. In a truly chilling fashion, Dr. Steinberg argues that, in order to prevent such tragedies, we need to stop worrying our heads about the civil rights of people with schizophrenia:
[W]e have too much concern about privacy, labeling and stereotyping, about the civil liberties of people who have horrifically distorted thinking. In our concern for the rights of people with mental illness, we have come to neglect the rights of ordinary Americans to be safe from the fear of being shot — at home and at schools, in movie theaters, houses of worship and shopping malls.
Dr. Steinberg makes a pejorative and unsubstantiated association here between schizophrenia and the mass shootings that have taken place in 2012. He refers to shootings “at home and at schools” (a clear reference to the December 14 Newtown, Connecticut massacre), “in movie theaters” (a clear reference to the July 20 Aurora, Colorado theater shooting), “houses of worship” (a clear reference to the August 5 shooting at a Sikh Temple in Oak Creek, Wisconsin), and “shopping malls” (a clear reference to the December 11 shooting at a shopping mall in Portland, Oregon).
Terrifying events, to be sure. But before we start tossing people’s civil liberties out the window, let’s look at whether any of the perpetrators of these violent acts actually had schizophrenia:
As far as we know, Adam Lanza, the Newtown shooter, was not diagnosed with schizophrenia, nor have we heard evidence that he was delusional.
James Holmes, the shooter in Aurora, saw a psychiatrist who specializes in schizophrenia — which means precisely nothing regarding his own diagnosis. Her practice was not limited to people with schizophrenia. He has not been diagnosed with the condition.
Wade Michael Page, who murdered six people at a Sikh Temple, was a racist skinhead who no one has ever remotely hinted showed signs of schizophrenia.
Jacob Tyler Roberts, who was responsible for the shooting at the mall in Portland showed no signs of delusional thinking to anyone around him, including his girlfriend.
But that doesn’t stop Dr. Steinberg from coming up with two new culprits:
At Virginia Tech, where Seung-Hui Cho killed 32 people in a rampage shooting in 2007, professors knew something was terribly wrong, but he was not hospitalized for long enough to get well. The parents and community-college classmates of Jared L. Loughner, who killed 6 people and shot and injured 13 others (including a member of Congress) in 2011, did not know where to turn.
Of course, Seung-Hui Cho was never diagnosed with schizophrenia in his lifetime. Psychiatrists like Dr. Steinberg have only done so post-mortem, and the more responsible ones acknowledge that they cannot make such a diagnosis with any certainty. The only mass murderer to whom Dr. Steinberg makes reference who has actually been diagnosed with schizophrenia is Jared Lee Loughner.
There are very good reasons that psychiatrists have to meet a client in person in order to render a diagnosis: second- and third-hand testimony is notoriously unreliable, and diagnostic assessments can take days to complete. Oddly enough, Dr. Steinberg seems to be aware that he is breaking the ethical standards of his profession by diagnosing people he has neither met nor treated:
I write this despite the so-called Goldwater Rule, an ethical standard the American Psychiatric Association adopted in the 1970s that directs psychiatrists not to comment on someone’s mental state if they have not examined him and gotten permission to discuss his case. It has had a chilling effect. After mass murders, our airwaves are filled with unfounded speculations about video games, our culture of hedonism and our loss of religious faith, while psychiatrists, the ones who know the most about severe mental illness, are largely marginalized.
As far as I can see, the only “unfounded speculations” here are coming from Dr. Steinberg. It is hard to imagine how an affluent psychiatrist in private practice could imagine himself to be “marginalized,” particularly when it comes to armchair diagnoses. Given that his entire piece further marginalizes an entire group of people who already far more likely to be the victims of violent crime than to be the perpetrators, the term rings especially hollow.
To his credit, Dr. Steinberg does acknowledge schizophrenia is not generally associated with violence, though he then turns around and contradicts himself:
The vast majority of people with schizophrenia, treated or untreated, are not violent, though they are more likely than others to commit violent crimes.
Dr. Steinberg rather skews the evidence here. In fact, people with schizophrenia are not more likely to commit violent crime when one factors in the presence of substance abuse. A PLoS study found that, when controlling for the presence of drug and alcohol abuse, people with psychosis are no more likely to commit violent crime that people without psychosis:
Importantly the authors found that risk estimates of violence in people with substance abuse but no psychosis were similar to those in people with substance abuse and psychosis and higher than those in people with psychosis alone. (Gulati et al. 2009)
In other words, people with no psychosis who abuse alcohol and drugs have a higher risk of committing a violent crime than people with psychosis who do not abuse alcohol and drugs, and a similar risk to people with psychosis who do. The factor to be looking at is drug and alcohol abuse, not schizophrenia.
That point seems to have been lost on Dr. Steinberg. He should know better. Shame on him.
References
ABC News. “Clackamas Town Center Shooting: Who Is the Alleged Shooter?” http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/video/clackamas-town-center-shooting-jacob-roberts-alleged-shooter-17959547. December 13, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012.
The Atlantic. “Diagnosing Adam Lanza.” http://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2012/12/diagnosing-adam-lanza/266322/#. December 13, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012.
Billeaud, Jacques. “Trial not likely for Jared Lee Loughner in 2012.” Boston.com, January 6, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012. http://www.boston.com/news/nation/articles/2012/01/06/trial_not_likely_for_jared_lee_loughner_in_2012/.
Gulati, Gautam, Louise Linsell, John R. Geddes, and Martin Grann. “Schizophrenia and Violence: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” PLoS Med 6, no. 8 (2009). doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000120.
Laris, Michael, Jerry Markon, and William Branigin. “Wade Michael Page, Sikh temple shooter, identified as skinhead band leader.” The Washington Post, August 6, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012. http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2012-08-06/world/35491487_1_end-apathy-sikh-temple-skinhead-band.
PBS News Hour. “Alleged Colorado Shooter Saw Schizophrenia Expert.” http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/social_issues/july-dec12/colorado_07-27.html. July 27, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012.
Psychiatric News Alert. “People With Schizophrenia More Likely to Be Victims, Not Perpetrators of Violence.” http://alert.psychiatricnews.org/2012/05/people-with-schizophrenia-more-likely.html. May 10, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012.
Steinberg, Paul. “Our Failed Approach to Schizophrenia.” The New York Times, December 25, 2012. Accessed December 27, 2012. http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/26/opinion/our-failed-approach-to-schizophrenia.html?_r=0.
Welner, Michael. “Cho Likely Schizophrenic, Evidence Suggests.” ABC News, April 17, 2007. Accessed December 27, 2012. http://abcnews.go.com/Health/VATec h/cho-schizophrenic-evidence-suggests/story?id=3050483#.UNxJWnfLBQF.
© 2012 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
Scapegoating in the Aftermath of the Sandy Hook Shooting: Yes, It’s Really Happening to Us
 Despite a number of clarifications in The New York Times and on ABC News, NBC News, and CNN that Asperger’s is not a predisposing factor for premeditated violence, the spurious association of Asperger’s with the violence in Newtown, CT is still strong. In part, the media is responsible for not having clarified early on that yes, Adam Lanza shot 27 people and yes, Adam Lanza was apparently autistic, and no, one had nothing to do with the other. Such failures were rife. For example, in exploring a possible explanation for the shooting, Dr. Xavier Amador opined on Piers Morgan Tonight that people with Asperger’s are missing an essential element of humanity:
Despite a number of clarifications in The New York Times and on ABC News, NBC News, and CNN that Asperger’s is not a predisposing factor for premeditated violence, the spurious association of Asperger’s with the violence in Newtown, CT is still strong. In part, the media is responsible for not having clarified early on that yes, Adam Lanza shot 27 people and yes, Adam Lanza was apparently autistic, and no, one had nothing to do with the other. Such failures were rife. For example, in exploring a possible explanation for the shooting, Dr. Xavier Amador opined on Piers Morgan Tonight that people with Asperger’s are missing an essential element of humanity:
Well, actually, a symptom of Asperger’s, and this is one report coming out which may or may not be true, is something’s missing in the brain, the capacity for empathy, for social connection, which leaves the person suffering from this condition prone to serious depression and anxiety.
But the media’s response is only a symptom of a much larger problem. Its willingness to blame Asperger’s is a reflection of a cultural association between disability and evil that has lasted for centuries. As Colin Barnes writes:
Throughout the Middle Ages, disabled people were the subject of superstition, persecution, and rejection. Haffter (1968) has pointed out that in medieval Europe disability was associated with evil and witchcraft. Deformed and disabled children were seen as ‘changelings’ or the Devil’s substitutes for human children, the outcome of their parents’ involvement with the black arts of sorcery. The Malleus Maleficarum of 1487 declared that these children were the product of the mothers’ intercourse with Satan… Protestant reformer Martin Luther (1483-1546) proclaimed that he saw the Devil in a profoundly disabled child. If these children lived, Luther recommended killing them.” (Barnes 2010, 21)
Nineteenth- and twentieth-century eugenicists picked up this connection between disability and depravity, believing “that there were genetic links between physical and mental impairments, crime, unemployment and other social evils” (Barnes 2010, 26). The linkage has come down to the present day in the pernicious belief that disability is synonymous with narcissism and anti-social behavior (Siebers 2011, 34-35).
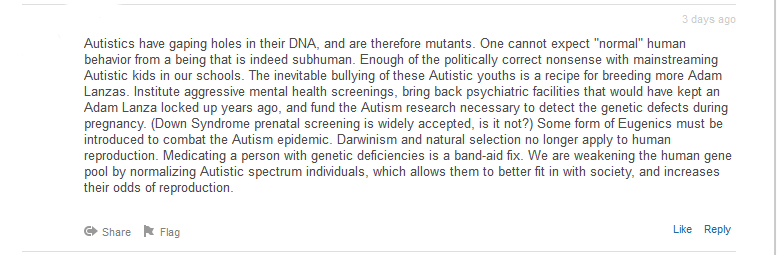
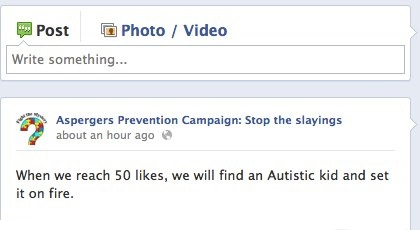
I’ve read a number of comments online that suggest that autistic people and autism parents are overplaying the scapegoating of Asperger’s. People say that the mainstream media has issued its clarifications and that the problem is solved. Unfortunately, it’s not that easy. Once this iteration of the cultural narrative about disability hit the airwaves, it quickly took root among ordinary people. Giving life to a well-worn untruth while people are in a state of nearly irrational fear is a difficult thing to undo. To give you a sense of just how deep the damage goes, I offer the following examples.
On the Volconvo forum, one commenter refers to people with autism and mental illness as “broken-minded defects” who are “dangerous” and whom society needs to monitor and imprison inside locked wards:
A commenter on a TIME article suggests that autistic people are “mutants” who need to be placed in “psychiatric facilities” and ultimately removed from the gene pool for the good of society:
And then there was the person who started a Facebook page and called for the killing of autistic children. (To its credit, Facebook quickly removed the page.)
This kind of scapegoating has begun the inevitable creep off the major news sites and social media and into the lives of ordinary autistic people and their families. Three friends have given me permission to share their experiences.
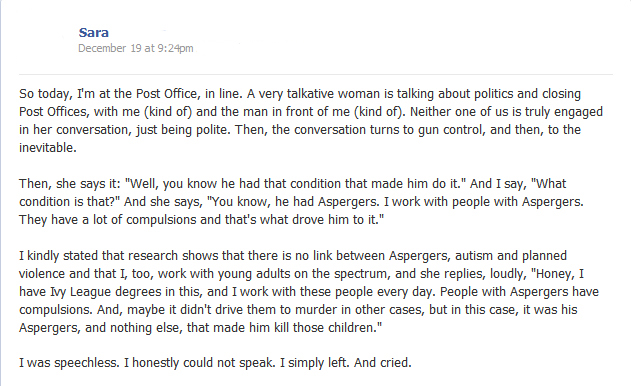
Here is the story told by my friend Sara, a woman with Asperger’s. While standing at the post office five days after the tragedy, she spoke to a woman, an Ivy League graduate, who said that Asperger’s — and Asperger’s alone — had caused the Sandy Hook shooting. Sara posted the following on her Facebook status:
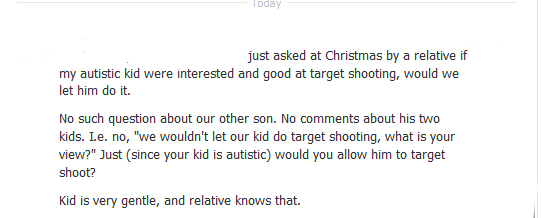
Another friend describes a situation in which a false belief in a link between autism and violence caused his wholly nonviolent autistic child to become suspect in the eyes of a relative:
Finally, my friend C describes a more frightening scenario. Her son J, who is 14 years old, had gone to Wal-Mart to look for a Christmas tree. He has Asperger’s and bipolar disorder, and people in his community are aware of his diagnoses. He was wearing headphones to block out sensory input, and, at one point, attempted to find a quieter place in the store. He had his hand on a price list in his pocket when someone who knew him went into a panic — a panic that resulted in the young man’s injury:
Like Trayvon Martin in his hoodie, the scary guy on the block appears to be, in the minds of some people, the kid with Asperger’s with his hands in his pockets. I’m just waiting for someone to suggest that, as Geraldo Rivera said about black men giving up their hoodies, young men with Asperger’s should wear pocketless clothing.
The stunning level of irrationality and fear being leveled at people with autism is tremendous cause for concern. In the face of this scapegoating, autistic people and autism parents are countering with positive images of autistic children and adults that show us as full human beings — ordinary, extraordinary, beautiful, and proud. To see these images, please go to the following Facebook pages:
Autism Shines
Autistics, Not Monsters
Disability and Representation
Let’s spread the word to end the scapegoating. And let’s keep doing it, now and always, wherever and whenever we can.
References
Barnes, Colin. “A Brief History of Discrimination and Disabled People.” In The Disability Studies Reader, edited by Lennard J. Davis, 20-32. New York: Routledge, 2010.
Christopher, Tommy. “Piers Morgan Quack Says People With Autism Lack Empathy: ‘Something’s Missing In The Brain’.” Mediaite, December 14, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://www.mediaite.com/tv/piers-morgan-quack-says-people-with-autism-lack-empathy-somethings-missing-in-the-brain/.
Facebook. www.facebook.com. Accessed December 24, 2012.
— “Autism Shines.” http://www.facebook.com/AutismShines?fref=ts. Accessed December 24, 2012.
— “Autistics, Not Monsters.” http://www.facebook.com/AutisticsNotMonsters?ref=ts&fref=ts. Accessed December 24, 2012.
— “Disability and Representation.” http://www.facebook.com/DisabilityAndRepresentation. Accessed December 24, 2012.
Falco, Miriam. “Groups: Autism not to blame for violence. CNN, December 19, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://www.cnn.com/2012/12/17/health/connecticut-shooting-autism/index.html.
Fox, Maggie. “Asperger’s not an explanation for Lanza’s Connecticut killing spree, experts say.” NBC News, December 18, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://vitals.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/12/18/15994353-aspergers-not-an-explanation-for-lanzas-connecticut-killing-spree-experts-say?lite.
Gilman, Priscilla. “Don’t Blame Autism for Newtown.” The New York Times, December 17, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/18/opinion/dont-blame-autism-for-newtown.html.
Nano, Stephanie. “Experts: No Link Between Asperger’s, Violence. ABC News, December 16, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory/experts-link-aspergers-violence-17987339#.UNj7VHfLBQG.
Rochman, Bonnie. “Guilt by Association: Troubling Legacy of Sandy Hook May Be Backlash Against Children with Autism.” TIME, December 19, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012. http://healthland.time.com/2012/12/19/guilt-by-associationtroubling-legacy-of-sandy-hook-may-be-backlash-against-children-with-autism/.
Siebers, Tobin. Disability Theory. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2011.
Volconvo. “Kindergarten isn’t just about identifying colors, shapes and sizes anymore.” http://www.volconvo.com/forums/society-rights/43038-kindergarten-isn-t-just-about-identifying.html. December 14, 2012. Accessed December 24, 2012.
© 2012 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg
It’s Happened Again: Apparently, It’s Let’s Publicly Defame a Family Member By Comparing Him to Adam Lanza Week
Last Friday, there was the infamous I Am Adam Lanza’s Mother piece.
This Friday, there is an equally disgraceful piece called My brother is not Adam Lanza, but he could be, in which the author, under her own name, with a photo of her brother, says that he could be the next Adam Lanza. Or that he could have been. If his parents hadn’t done such a good job. And he weren’t such a nice person. Or something.
Please, dear readers, answer me two questions: What makes people unable to restrain themselves from blowing the privacy of family members? And what compels them to put a photo of a family member in a piece in which said family member is likened to Adam Lanza?
The author acknowledges that Asperger’s isn’t associated with violence. She acknowledges that her brother, who has Asperger’s, has never committed a violent act in his life. The closest he has ever come has been to get up into her face, with his fists, once.
It was only years later as I watched my brother shaking with rage, as he struggled to hold himself together, with his fist clenched inches from my face that I understood how intense frustration and pain could explode out of a person.
…
He has never hit me, or any family member, although there are times he uses up every ounce of self- control restraining himself. This incredible effort and bravery, is testament to his goodness.
On these rare occasions I wonder what it would take to push him over the edge. Is that the difference between him and Adam Lanza?
So, apparently, in the mind of Pamela Mirghani, shaking with rage at a family member, if the person shaking with rage happens to have Asperger’s, suggests a risk for committing mass murder. I can’t even begin to parse the logic there, because there isn’t any. The statement is completely prejudicial. Does she realize how many non-autistic people get up in other people’s faces with their fists, and worse, and don’t go on to shoot up schools?
Millions of people, all over the world, feel like hitting people and they don’t do it. And millions of people, all over the world, feel like hitting people and — unlike her brother — they do. Does that make all of these people potential mass murderers? Of course not. And even if it did, why in God’s name link it to Asperger’s, especially when she admits that Asperger’s isn’t linked to violence at all:
While violence may not be linked to autism, frustration is. Without the tools, help and support to cope with that frustration it can overwhelm the sufferer.
I am not Adam Lanza’s sister. My brother is NOT Adam Lanza. But he could have been, maybe could still be under certain circumstances. And acknowledging this is not wrong.
Yes, folks. She just said that her brother with Asperger’s, who has never been violent, who on “rare occasions” has gotten so upset that he wanted to hit someone, could become a mass murderer under certain circumstances — purely because his Asperger’s makes him frustrated. Of course, that blithely ignores the fact that all studies show that Asperger’s is not associated with premeditated violence, and that there is no evidence that mere frustration makes someone load weapons into his car, drive to a school, and commit murder and mayhem. But hey, who needs studies — not to mention common sense — when you can defame and violate the privacy of a family member for no good reason?
So yes, Pamela. Acknowledging something, when it’s entirely false, prejudicial, and defamatory, is wrong. Saying that anyone with Asperger’s could become a mass murderer under certain circumstances, simply because the person has Asperger’s, is wrong. Saying that your own brother could become a mass murderer, merely because he shares a diagnosis with someone who just committed an unthinkable act, is wrong. There is nothing about Asperger’s that predisposes people to premeditated violence. Nothing at all.
To suggest that your brother with Asperger’s is capable of such a thing, purely because of his disability, not only tars and feathers him, but also tars and feathers everyone who has Asperger’s.
Do you know what that means? Do you know the harm that could come from articles like this one? Do you know the kind of fear that autistic people are feeling right now because we’re being scapegoated in the media for the evil that was done last week? Any idea at all? Do you know how this stigmatizes your brother? Do you understand the humiliation involved in calling him a potential mass murderer? Do you grasp the fact that it puts your brother — and all of us — in potential danger for you to say such a thing in public?
Great job, Pamela. What a nice Christmas present to your brother, to autistic people, and to those who love us. Merry Christmas to you, too.
References
The Huffington Post. “‘I Am Adam Lanza’s Mother’: A Mom’s Perspective On The Mental Illness Conversation In America.” http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/12/16/i-am-adam-lanzas-mother-mental-illness-conversation_n_2311009.html. December 16, 2012. Accessed December 16, 2012.
Mirghani, Pamela. “My brother is not Adam Lanza, but he could be.” National Times. December 21, 2012. Accessed December 21, 2012. http://www.watoday.com.au/opinion/my-brother-is-not-adam-lanza-but-he-could-be-20121221-2bql1.html.
Note: Anyone who would like to protest the nature of Pamela Mirghani’s article is welcome to share a link to this piece in an email to news@watoday.com.au. You can also find WA Today, on whose site the piece appears, on Twitter at @watoday.
© 2012 by Rachel Cohen-Rottenberg